Completion requirements
2. Introduction to corruption and timber trafficking
2.2. Infographic: impacts of timber
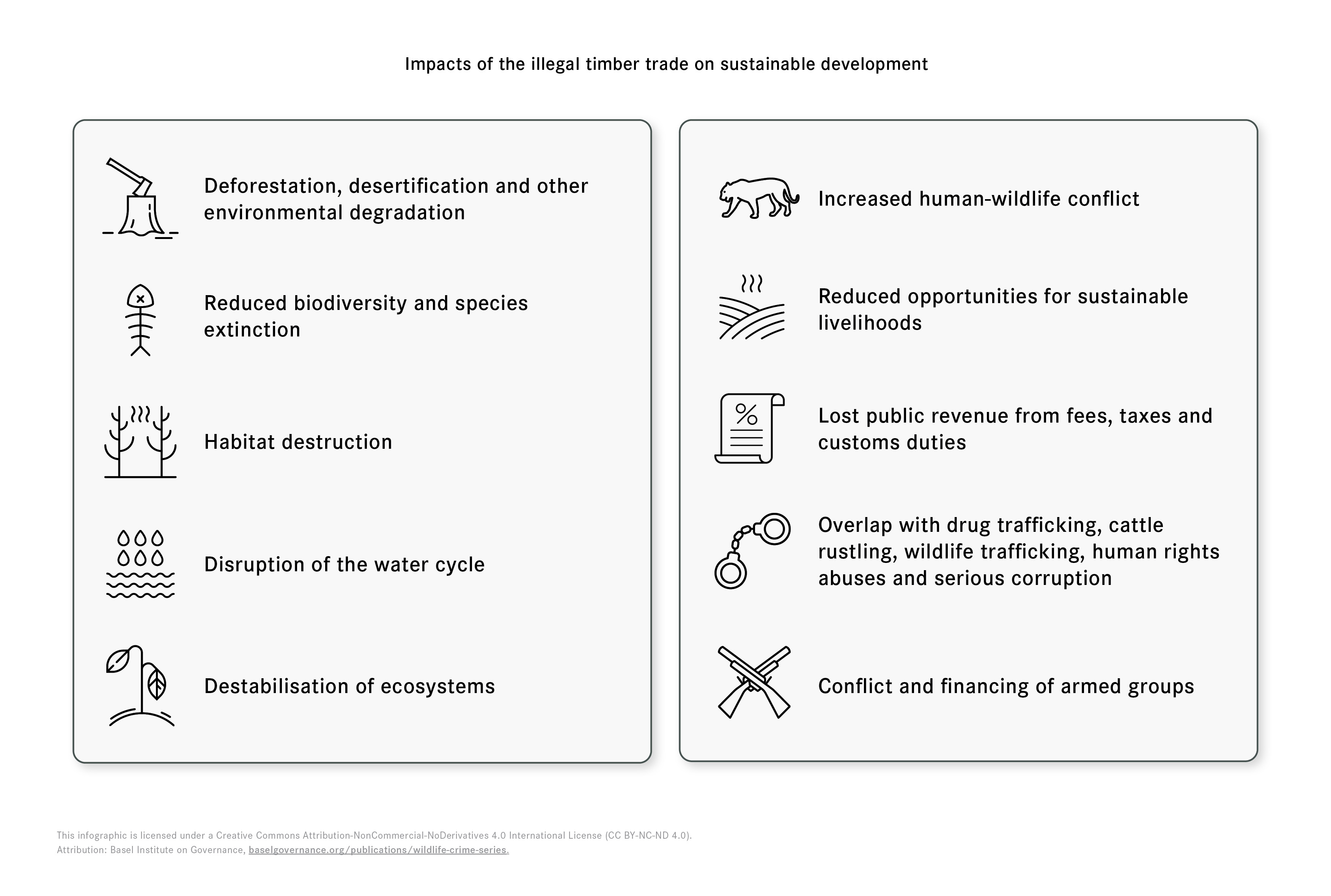
Timber
trafficking has numerous detrimental effects on sustainable and equitable
development, including the following (Dawson,
2020; UNODC, 2012; WWF, n.d.):
- contributes to deforestation, desertification and other forms of environmental degradation;
- reduces biodiversity with the potential for species extinction;
- destroys habitats;
- increases human-wildlife conflict due to the destruction of habitats.
- robs communities of the opportunity to harvest renewable forest resources and achieve sustainable livelihoods;
- deprives governments of billions in fees, taxes and customs revenues;
- often overlaps with other illegal activities involving drug trafficking, cattle rustling, wildlife trafficking, human rights abuses and serious corruption;
- fuels conflicts in areas where armed groups engage in timber trafficking and the taxation of the movement of illegal timber harvests, such as in Myanmar and Senegal;
- destabilises ecosystems by disrupting the water cycle.